GWBplugin – Getting started with C++
The GWB plug-in feature is implemented as a Dynamic-Link Library (DLL). For C++ we provide a GWBplugin wrapper class contained in the header file GWBplugin.h and the GWBplugin.dll export library GWBplugin.lib to link against. This page answers common queries about how to use the C++ version of the plug-in feature.
Using the plug-in
Using the GWB plug-in feature:
- Compiling your program and linking to the GWB plug-in library.
- GWBplugin C++ wrapper class overview.
- Initializing the GWB application you wish to use.
- Configure and execute your calculations.
- Retrieving the results.
Compiling your program and linking to the GWB plug-in library.
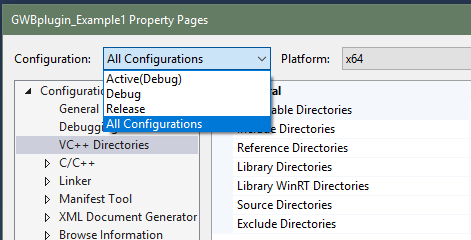
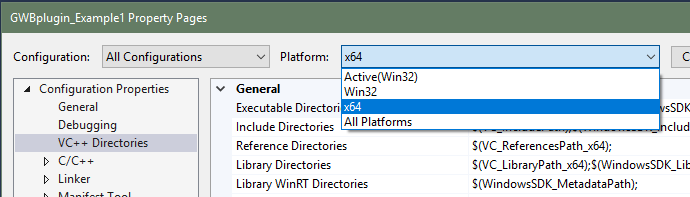
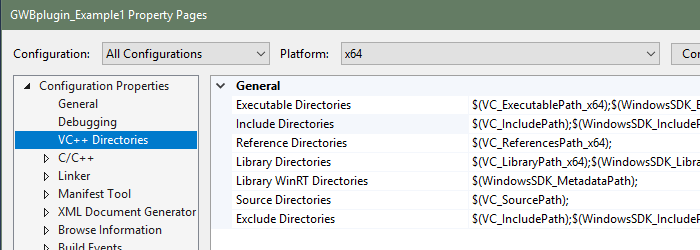
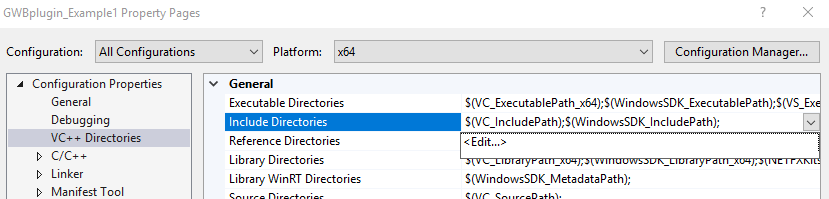
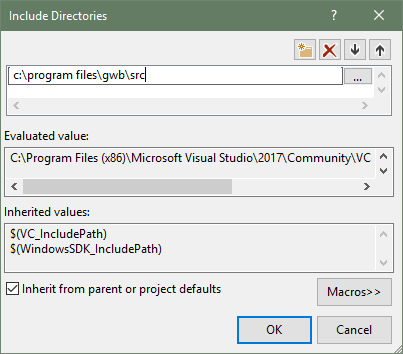
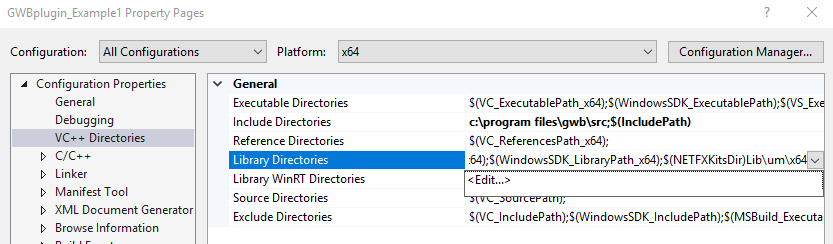
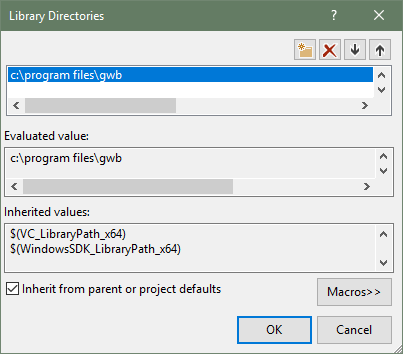
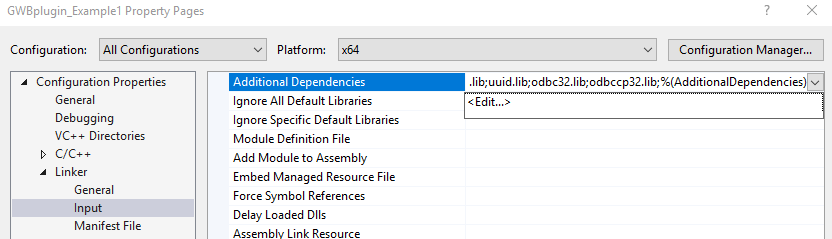
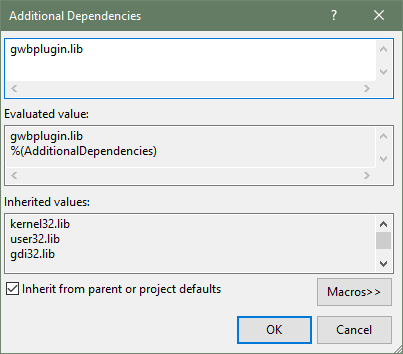
The GWB plug-in has been tested on C++ compilers from Microsoft, Intel, and GCC. The header file GWBplugin.h you need is installed to your computer in the "src" directory of the GWB directory. The library you need to link to GWBplugin.lib is installed in the GWB directory (in earlier versions of GWB the library file was also in the "src" directory). For step-by-step instructions on setting up your build environment and examples using the Visual Studio command line, Visual Studio, and MinGW/MSYS/g++ please see the Quickstart tutorials and examples.
GWBplugin C++ wrapper class overview.
This is a synopsis of the C++ wrapper class provided in GWBplugin.h in the "src" directory of the GWB installation folder.
// GWBplugin.h
#define ANULL -999999.0 // marker for an undefined value
class GWBplugin {
public:
GWBplugin();
~GWBplugin();
int initialize(const char* app_name, const char* file_name = NULL, const char* cmds = NULL);
int exec_cmd(char* uline);
int results(void* data, const char* value, const char* units = NULL , int ix = 0 , int jy = 0);
};
Initializing the GWB application you wish to use.
Within your code you must first create a "GWBplugin" object. Next, use the "initialize" function to start the GWB application of interest by passing the application name, a optional file name for the GWB application to write output to, and any command-line type arguments.
Configure and execute your calculations.
The "exec_cmd" function can be used to transmit commands to the plug-in. Each application has a chapter in the reference manual of the documentation on what commands are available. You use these commands to configure the application and then send a "go" command to trigger the calculations.
Retrieving the results.
Retrieving the results using the GWB plug-in feature can be accomplished using the "results" function. The keywords, default units, and return types are the same as those listed in the Report Command chapter of the reference manual in the documentation. To use the "results" function you provide the address of a data block to fill, along with the desired report command and keywords, optional desired units, and the node location of choice (X1t and X2t only).
Quickstart tutorials and examples
Step-by-step instructions for compiling GWBplugin Example 1 on the command line with the Microsoft or Intel compiler.
Step-by-step instructions for compiling GWBplugin Example 1 on the command line with MinGW, MSYS, and g++.
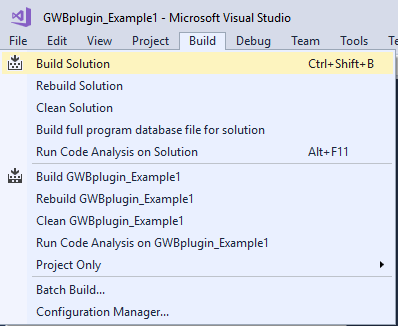
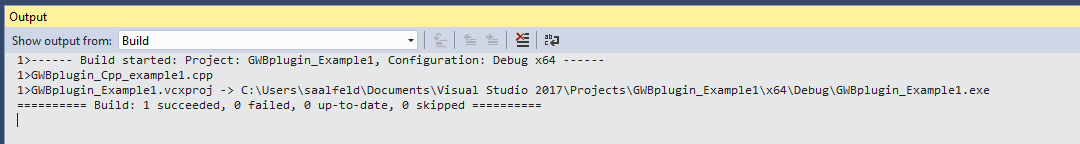
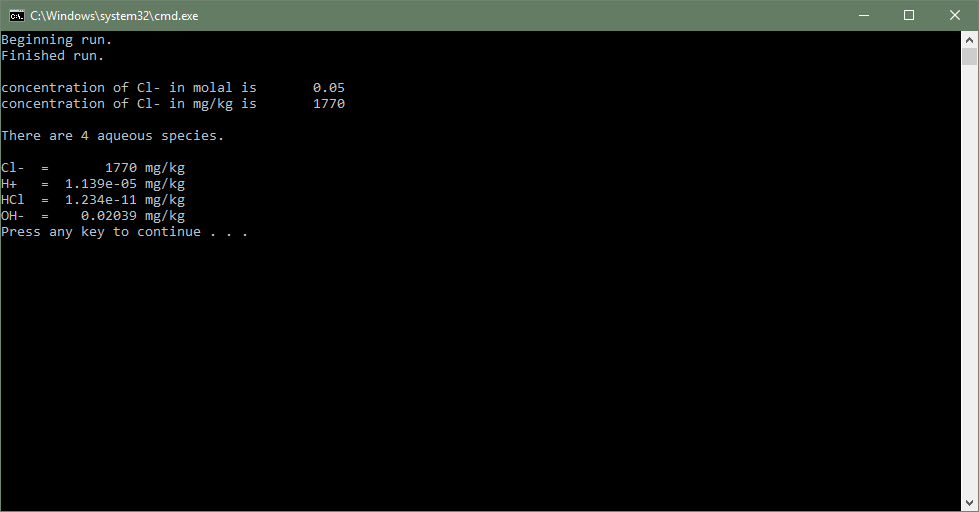
Step-by-step instructions for compiling GWBplugin Example 1 in Microsoft Visual Studio 2017.
C++ plug-in support
What C++ compilers are supported by the GWB plug-in?
The plug-in has been tested using compilers from Microsoft, Intel, and GCC.
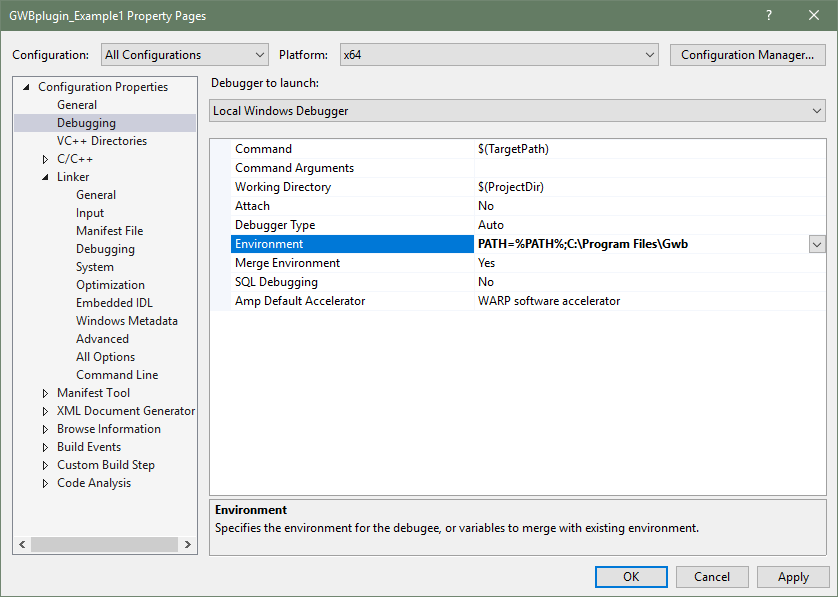
Why does it say it can't find the GWBplugin.dll when I try to run my program?
In order to locate the GWB DLLs that the GWBplugin class uses you must add the GWB installation directory to the PATH environment variable.
Where are the GWBplugin files that I need to link against located?
The GWBplugin export library (GWBplugin.lib) is installed to the GWB directory and the header file (GWBplugin.h) is installed to the "src" folder in the GWB directory.
In some previous versions of GWB the export library was also in the "src" folder.
Why does my compiler say that it can't find the GWBplugin library to link against even though I am using the full path to link?
This result is commonly caused from using a 32-bit compiler to link against a 64-bit library, or vice versa. Check to ensure the version of the compiler you are using is the same as the version of GWB you installed.
For answers to additional questions please check the plug-in section of the reference manual in the documentation, our main support FAQ, or contact us.